Current Research in the Xue Lab
Research in the Xue lab is focused on understanding conserved mechanisms of DNA replication and damage repair using methods of biochemistry, genetics, cell biology, and structural biology.
Smc5/6 Sumoylation Project
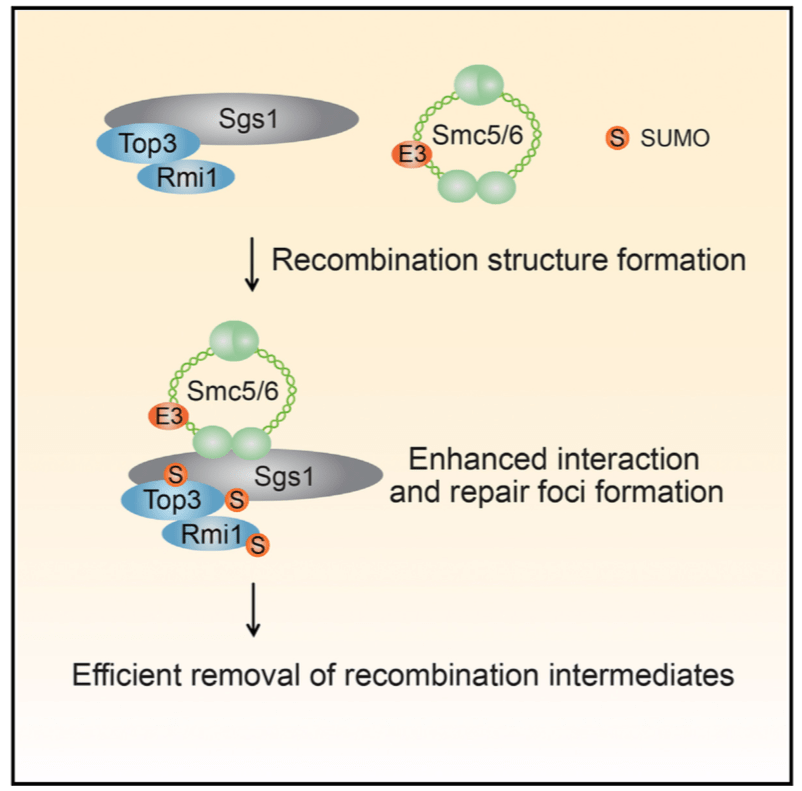
This project investigates the function of protein sumoylation in DNA damage repair. Sumoylation is the process by which proteins are post-translationally modified to alter their activity with SUMO (a small ubiquitin-like modifier). The Nse2/Mms21 subunit of the Smc5/6 complex acts as a SUMO E3 ligase, demonstrating sumoylation activity on Sgs1 helicase of the STR complex, leading to the promotion of DNA damage repair. A deeper exploration into the Nse2 sumoylation mechanism and the factors that regulate sumoylation activity is ongoing.
ZGRF1 Project
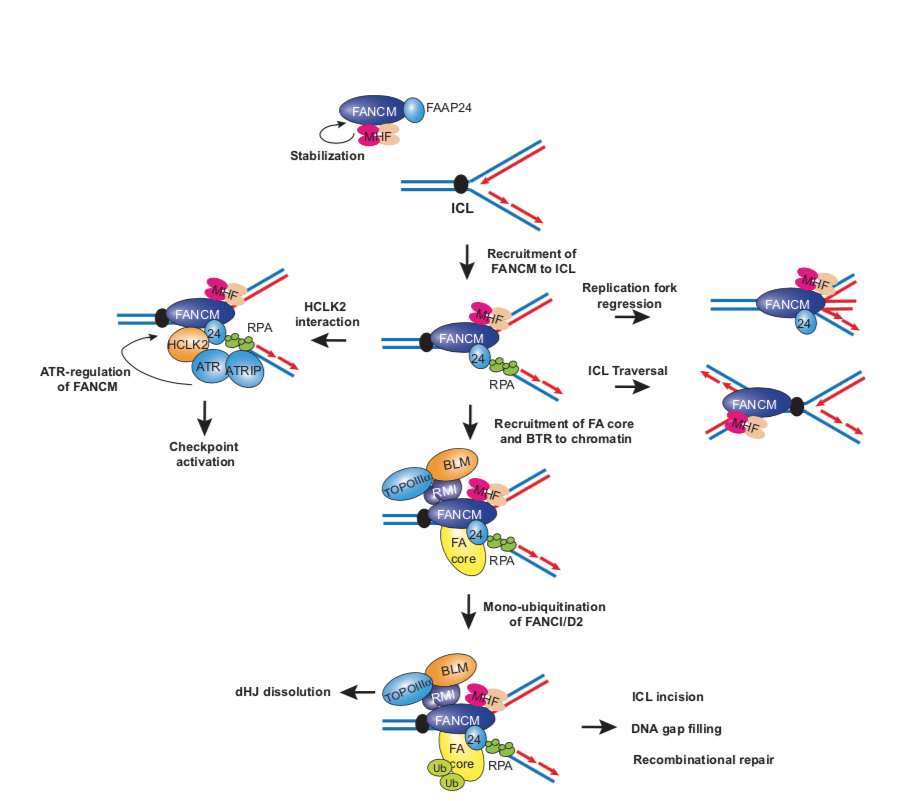
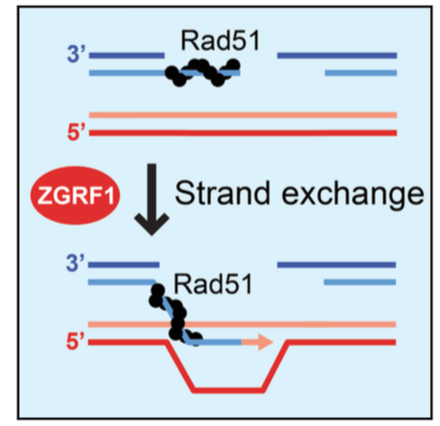
This project aims to explore the underlying mechanisms and roles of nucleic acid motor protein ZGRF1 helicase in chromosome damage repair and disease avoidance. ZGRF1 plays a critical role in the Fanconi Anemia (FA) repair pathway and the double-strand break (DSB) repair pathway, Homologous Recombination (HR). ZGRF1 interaction with other HR repair factors, including the well-known BRCA1 protein, highlights it as a novel potential therapeutic target for the treatment of diseases such as Fanconi Anemia, neurodegenerative diseases, and familial breast and ovarian cancers. Further characterization of ZGRF1 activity and its binding partners could reveal more layers in the continuing investigation into physiological mechanisms of genome maintenance leading to or preventing tumorigenesis.

UAP56-ALYREF Project
The UAP56-ALYREF project examines the R-loop resolution activity mediated by UAP56 helicase and promoted by the mRNA export adapter ALYREF. R-loops are complex nucleic acid structures containing both DNA and RNA. These structures pose threats when left unresolved by adding tension to the genome leading to DSBs, replication fork collapse, and premature transcription termination. UAP56 is an RNA-DNA helicase that can resolve R-loops by unwinding the RNA strand from the duplex DNA. When interacting with ALYREF, UAP56 R-loop resolution activity is promoted, increasing the efficiency of R-loop removal. R-loop biology is a swiftly growing field of research, particularly maintaining an appropriate level of R-loops to balance beneficial physiological roles with pathological roles.